SAM Terms & Definitions
[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" admin_label="row" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Competence" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]01
The SAM6™ Process, Step 1: Competence
The first step in the SAM 6 process is competence.A competent marketer has a clear understanding ofthe broad concept of marketing, as well as a workingknowledge of specific marketing terms.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]02
Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix consists of the four Ps of marketing: -Product -Price -Place (distribution) -Promotion [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]03
Promotional Sequence
The Promotional Sequence consists of six categories: company, product, market, message, messenger and promotional mix.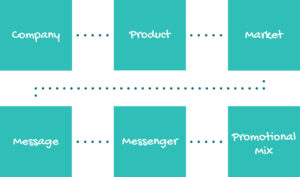 [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]04
Promotional Mix Channels
Almost all promotions will fit into one of the following five promotional mix channels: 1. Media coverage, both traditional & digital 2. Website 3. Social Media 4. Advertising 5. Personal Selling[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Brand" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]05
Brand
A brand is the definition consumers hold in theirmind of a company and its products. A brand is builtin two ways, by what the customer is told, and bywhat the customer experiences.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]06
The SAM6® Process, Step 2: Code
The second step in the SAM 6 process is developing code sheets. Code sheets are a means of gathering and documenting important information about your company and the products it promotes. Code sheet can also be made for specific offers. Code sheets help direct and control your creative staff.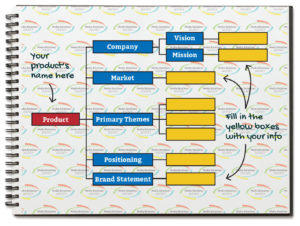 [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]07
Communication Process
In the Communication Process, a sender wants to communicate a message to a receiver. The sender encodes the message. Then the message is decoded by the receiver.08
Institutional Advertising
When marketers use promotions to support acompany in general, it is commonly referred to asInstitutional Advertising.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Company Vision" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]09
Company Vision
A company’s vision defines how a company will lookand what it will be in the future. It’s what it one dayintends to become. By definition, a company doesnot currently match its vision. Companies draftvision statements as a basis for aligning activities.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]10
Company Mission
A company’s mission is a statement that encapsulates HOW a company intends to achieve its vision. Vision Statement: This is what we are going to become. Mission Statement: This is how we are going to do it.[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]11
The SAM6® Process, Step 3: Channels
The third step in the SAM 6 process is selecting the appropriate Promotional Mix channels. The Promotional Mix channels you choose to employ depend on many variables including your message, the market and your resources. These are the five channels in the Promotional Mix: Publicity Website Social media Advertising Personal selling[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]12
Consumer Buying Process
The Consumer Buying Process describes the steps that consumers go through as they decide whether to purchase and keep a product. This process follows a predictable pattern. Smart marketing will address the different steps in the Consumer Buying Process.13
Product Mix
The Product Mix is a table that categorizes a company’s products into “product lines”. Large companies with many products may have groups of lines called silos or platforms.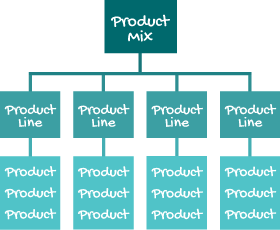 [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]14
Marketing Segmentation Strategies
Markets are often be divided into segments of similar groups called submarkets. But how many submarkets should a market be divided into? Three? Eight? Fifty? None at all? Consider these four strategies: Undifferentiated targeting strategy: Using one promotional strategy for all marketing segments Concentrated targeting strategy: Tailoring promotions only to the most lucrative marketing segments Multi-segmented targeting strategy: Creating unique promotions to multiple market segments Micro-segmented targeting strategy: Marketing to one specific individual [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]15
Marketing Segmentation Variables
Market Segmentation Variables are characteristics and elements used to build a profile or persona of a marketer. Here are some main categories: Demographic: age, gender, income, ethnicity, family lifecycle. Geographic: geographic location such as city, state, region, etc. Psychographic: a mindset such as surfers, health conscious, political orientation, etc. Benefit sought: low price, high quality, quick delivery, best color, etc. Usage rate: frequent buyer, on-time buyer, sporadic buyer, moderate buyer, etc. Geodemographic: combines psychographic and geographic, for example, New York business people think differently than Montana ranchers. [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]16
Generational Categories
Seniors: Prior to 1945 Baby Boomers: 1946 – 1964 Gen X: 1965 – 1979 Millennials: 1980 – 1994 Post Millennials or Gen Z: 1995 – early 2000s[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]17
Innovation Adopter Curve
 Innovators: Immediately adopt and even think up new products and trends.
Early Adopters: Quick to adopt the products and trends. Little loyalty because their nature is to move on to new products and trends.
Early Majority: Open to trying some new products and trends but watch which way the wind blows before they decide. Not everything the early adopters do catches on with this group. They are loyal but open to change.
Late Majority: Skeptical. Will use products and trends only after they appear to be accepted by the mainstream. Loyal and slow to change.
Innovators: Immediately adopt and even think up new products and trends.
Early Adopters: Quick to adopt the products and trends. Little loyalty because their nature is to move on to new products and trends.
Early Majority: Open to trying some new products and trends but watch which way the wind blows before they decide. Not everything the early adopters do catches on with this group. They are loyal but open to change.
Late Majority: Skeptical. Will use products and trends only after they appear to be accepted by the mainstream. Loyal and slow to change.
Laggards: Hold on to the old and resist the new. Valued customers when a product is in the decline stage of the product lifecycle. [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Primary and Secondary Value Points" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
18
Primary and Secondary Value Points
Primary Value Points are the top one, two or three(maybe as many as 5) reasons why consumerspurchase a product. These should be prioritized inorder of significance.Secondary Value Points are all of the less commonreasons people purchase a product.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Unique Selling Proposition" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]19
Unique Selling Proposition
The Unique Selling Proposition is a claim yourproduct can make that none of your competitors can.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]20
The SAM6® Process, Step 4: Calendar Schedule
The fourth step in the SAM 6 process is scheduling your promotions on a calendar. [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]21
Positioning
Positioning is how your product is positioned in the mind of the consumer compared to the competition. Some factors that may be a part of your product’s Positioning include: Price Quality Speed of delivery Convenience[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Brand Statement" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]22
Brand Statement
A Brand Statement is a short paragraph written inthe words a customer would use if you overheardthem describing your product to another person, andthey got it exactly right.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]23
AIDA
A – Attention I – Interest D – Desire A – Action The acronym AIDA is a classic, time-honored format that can be followed to create an effective promotional message. AIDA is a helpful tool for producing promotional communications that will be compelling to consumers.[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]24
Features/Benefits/Desires
Feature: a distinctive attribute or aspect Benefit: an advantage gained from something Desire: a strong feeling of wanting something or wishing for something to happen [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]25
The SAM6® Process, Step 5: Control Template
The fifth step in the SAM 6 process is developing a control template for your creative team. Your control template provides the guidelines for your writers, designers and other creative staff to follow. The control template allows these imaginative professionals to create attention-getting content without losing site of the marketing necessities. [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]26
Product Lifecycle
The Product Lifecycle is the period of time a product exists in the marketplace from its introduction to its discontinuation. The Product Lifecycle consists of four stages: Introductory Growth Maturity Declining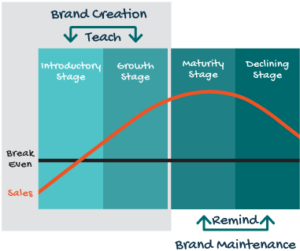 [/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]27
Push & Pull Marketing Strategies
Push strategy: Promotions within the distribution channel that causes consumers to be aware of the product. Example: a distributor offers retail stores a free boat they can use as a giveaway promotion if they buy a pallet of product and display it in the boat in their store. Pull strategy: Promotions directed right to the consumer. This causes customers to go to the store and buy the product or ask the stores to stock it if they don’t already. Consumer demand can cause a store to stock a product. This happened when we had an article run for Breathe Right Nasal Strips in an area where Target didn’t stock them. Target was flooded with requests, so they began stocking the product.[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure="1_3,1_3,1_3" _builder_version="4.16" background_size="initial" background_position="top_left" background_repeat="repeat" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_code admin_label="Term Marketing Environment" _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]28
Marketing Environment
The Marketing Environment consists of factors thatare beyond your company’s control, such as theeconomy, the competition’s technology level, majorweather disturbances or world events. Marketerscannot control everything that happens in theoutside world. Instead, they must understand howthe external environment is changing and how thatchange will impact the market.[/et_pb_code][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.16" global_colors_info="{}"]29
Reach & Frequency
Reach: The size of the target audience exposed to a message.
Frequency: Number of times the target audience is exposed to a message.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type="1_3" _builder_version="4.16" custom_padding="|||" global_colors_info="{}" custom_padding__hover="|||"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.24.0" global_colors_info="{}"]